
Today (NST)
Friday, Apr 25, 2025
Smart Search
Please post in your Technical Queries, Comments & Suggestions to Contact us......
Advertisement

For Advertisement
|
|
| Subscribe to BREINS Sci-Tech |
| Visit this group |

Seismic Resistant Design
Structural Configuration & Damage
Columns those are short-heighted or with shorter effecitive heights to that of the other regular (taller) columns within the same storey are called Short Columns. Formation of Short Columns could be due to presence of intermediate beams or due to other reasons as shown in Figs-11, 12 & 13 below. These are the typical cases that introduce Short Columns in buildings. In general, there would be presence of Short Columns wherever effective column heights vary within the same storey due to various structural configurations or boundary conditions.
Short columns are relatively stiff in comparison to other regular columns due to their lower effective heights hence have increased Seismic Demand. These columns attract higher value of earthquake induced forces than their counterparts; thereby making it highly vulnerable in earthquakes. This effect is termed as "Short Column Effect" in frame structures.
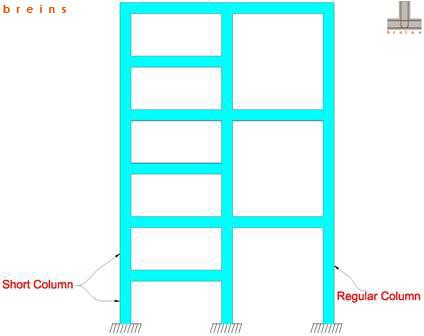
Fig-11 (Formation of short columns due to intermediate staircase landing beams in between two floors)
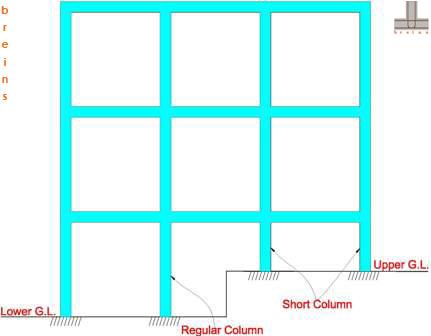
Fig-12 (Formation of short columns due to variation of column heights at the ground floor due to difference in ground level)
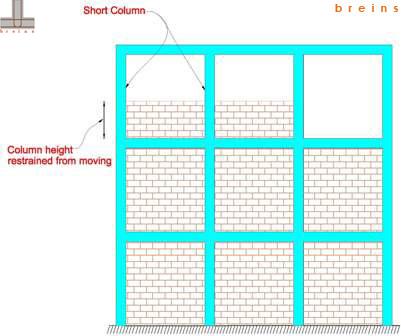
Fig-13 (Formation of short columns due to partial height of brick masonry infill walls)
Short Columns demand special attention in building structures. As far as possible, such configuration shall be avoided during planning phase itself; as failure of such columns could be quite brittle in nature hence disastrous. In RC structures, special shear confining reinforcements are necessary in such columns.
As we have seen earlier in the Eqn (1) that higher the structure's mass, higher will be the earthquake induced forces on it. So lowering the structure's mass is the another important aspect in ERD. Light-weight structures experience lower value of earthquake induced forces.
In building structures, brick masonry partition walls are the main contributor in the overall building's mass. In modern high rise buildings use of light weight prefab panels (Fig-14) in-place of brick masonry walls have been in practice for long time. Also, hollow concrete blocks (Fig-15) could be used to acheive the benefit of its light weight.

Fig-14 (Installation of ultra light-weight prefab panels as partition walls in-place of brick masonry walls to reduce earthquake forces on the building : Light-weight buildings are safer in earthquakes)

Fig-15 (Hollow concrete block, used instead of bricks in partition walls because of its light-weight and good thermal insulation)
Irrespective of all these unsymmetricities, irregular shapes & vertical irregularities in building configuration it can be made safe in earthquake if proper modeling and analysis of the concerned structure were carried out.
However, it should be noted that the selection of regular building configurations and the application of sound detailing principles are more likely to provide the required level of security against collapse than detail refinement of the analysis techniques.